RISK FACTORS FOR COMMUNITY ONSET CENTRAL LINE ASSOCIATED BLOODSTREAM INFECTIONS (CO-CLABSIS) IN PEDIATRIC ONCOLOGY PATIENTS
METHODS: We conducted a case-control(1:2) study at a pediatric oncology hospital in Athens,Greece(12/2015-12/2017).Cases were defined as all patients with a central line(CL) and a BSI on the day of admission or the day after without a secondary focus of infection.Controls were selected from patients that visited the outpatient clinic(OC) the same day.Clinical and demographic characteristics including type of CL,time since placement,underlying disease,number of OC visits and the number of times the CL was accessed the previous week were recorded.Associations were evaluated using the chi-square test of independence and the Mann-Whitney test.
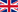
RESULTS: Thirty-one cases and 56 controls were identified. Univariate analysis showed that factors found to be correlated with a higher probability of a COCLABSI were a) Acute non lymphoblastic leukemia(AnLL) (88.89%) Vs. other cancer type,p=0.002) b) double lumen tunneled CL(42.62%) Vs. single,p=0.014 and c) neutropenic status (50.00%,p=0.007) (Table 1). Conditional multivariate logistic regression revealed that AnLL patients are 38 times more likely to to develop a COCLABSI (95%CI 1.87-772,p=0.018), patients with a double lumen CL 27 times(95%CI 1.71-431,p=0.019) and neutropenic 5 times (95% CI 1.11-24.02,p=0.036).
CONCLUSIONS: Factors such as Acute non-Lymphoblastic Leukemia, double lumen tunneled catheter and neutropenia increase the likelihood for a COCLABSI. After multivariate analysis AnLL, CL type and neutropenic status were independently associated with a COCLABSI. However the sample size may have limited our ability to detect other significant risk factors.